AI agents have quickly taken over the business landscape as the frontier of agentic transformation. Processes that were once constrained by static code or limited by headcount can become agentic workflows that accelerate growth, reduce costs, and mitigate risk.
But the question many teams face isn’t whether AI agents can help, it’s how to start. You don’t need a large company-wide transformation as the first step, in fact, you can hit the ground running by starting small with low complexity but high value end-to-end use cases.
1. Choose the Task
Take a moment to list the top 10 most frequent tasks that you need to do for your job. Then look for tasks that are manual, repetitive, and/or error-prone. As we share in our ultimate guide, AI agents are well-suited for tasks that go beyond simple logic or static rules. Identify tasks that require more than just basic automation, and ones that involve decision-making, context awareness, and coordination across systems. From this shortlist, identify one end-to-end task that is best suited for automation.
Example: Invoice reconciliation is a process where three documents (purchase order, goods receipt note, and vendor invoice) are compared before payment is approved. If all three match, the invoice is cleared for payment, and it is flagged for review if all three do not match.
2. Define Success
Any successful AI agent implementation should have a clear objective and measurable outcome. Is it saving time? Reducing errors? Cutting costs? Having a measurable goal makes it easier to evaluate the impact of integrating AI agents into your workflows. The goals you define here are critical, since agents are goal-oriented software systems.
Example: One measure of success by automating 3-way invoice matching is saving time. Instead of spending hours on manual review, more focus can be shifted towards higher-value work that drives the business forward such as strategic planning.
3. Map the Agent’s Workflow
With your task at hand, visualize the manual workflow from start to finish. This means breaking down the process into step-by-step instructions to get your task completed. Identify where decisions need to be made, what events or conditions trigger each step, and whether the task will require your agent to integrate with systems, applications, and data sources.
Oftentimes, you may find there’s no well-defined workflow. In that case, look for alternative ways to capture the information and distill it. For example, you could record a session with teammates where you talk through the process out loud, then use the transcription to help map the workflow.
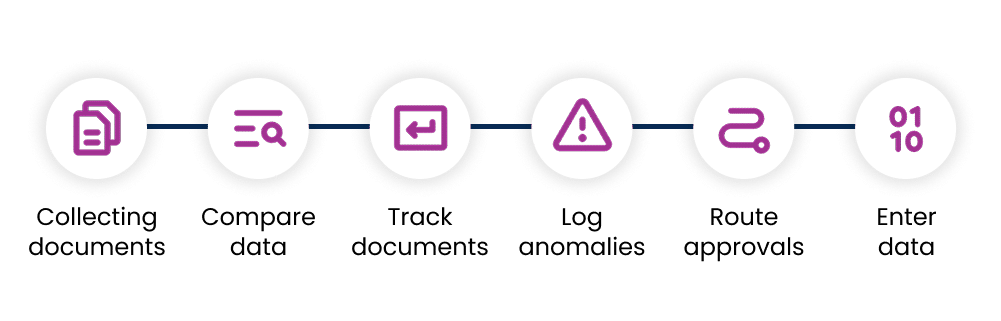
Example: Invoice reconciliation, a potential workflow could look like hunting for purchase orders across different sources, comparing items line-by-line, tracking down delivery documents from the warehouse management system (WMS), logging discrepancies, routing approvals, entering enterprise resource planning (ERP) data, escalating exceptions, and maintaining audit trails.
4. Identify the Governance and Tools Needed
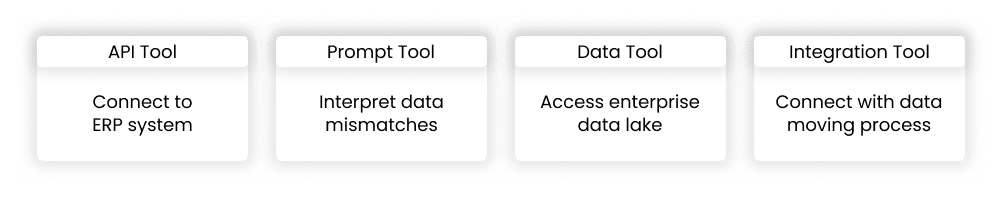
Most tasks that can be automated often require integrations with existing applications, access to specific APIs, or connections to internal and external data sources. For AI agents, these actions are in the form of tools. Most tools can be categorized into four types: API, prompt, data, and integration. This means that you’ll need to equip an agent with tools in order for it to take any real action. This is one of the reasons why governance is critical. AI agents need to be controlled to prevent security breaches and ensure it is accessing the appropriate tools for appropriate actions. Features such as centralized agent registry, anomaly detection, and detailed telemetry logs support responsible AI and help govern agents.
From there, you’ll need to choose an AI agent management solution that is compatible, can connect to your enterprise systems, and has the governance capabilities needed for responsible AI. Pinpointing these requirements ensures your AI agent can operate effectively within your environment and that you have full visibility and control.
Example: An invoice reconciliation agent may need an API tool to connect with ERP systems to fetch purchase orders, a prompt tool to interpret mismatches, a data tool to access trusted enterprise data lake that provides context for reconciliation, and an integration tool which ensures the agent can move data between ERP, WMS, and payment systems without disruption.
To build AI agents that can truly take action, they must be integrated with your business applications, enterprise data, and secure APIs, the very foundation provided by the Boomi Enterprise Platform. Building on this, Boomi Agentstudio empowers organizations to simply design, govern, and orchestrate all AI agents at scale with a no-code experience and enterprise-grade security. Start a free trial today.
5. Design the Agent, Apply Guardrails, and Test for Validation
Once you have decided which AI agent management solution to use, it is time to design your agent, create the tools it needs, and connect it to enterprise systems. But more importantly, governance needs to start from day one.
Ensure your agent behaves responsibly and operates within the appropriate parameters by applying guardrails. This means setting precise rules, restrictions, and filters, effectively embedding your agent with responsible AI principles such as protecting data privacy. It’s also best to build and test your AI agent in a controlled environment to ensure it works properly without disrupting live business processes. Be sure to pay attention to where the agent excels and where human judgement is still critical.
Example: An invoice reconciliation agent may have limits on approval amounts, so that it cannot approve invoices above a certain value without human review.
Agent Designer in Boomi Agentstudio can automatically generate an agent draft based solely on a goal provided by the user in natural language. You can then quickly fine-tune all aspects of your agent such as instructions, tools, and guardrails, and use the convenient test environment to instantly evaluate your agent and make changes easily.
6. Deploy and Govern
After your agent is approved for use, deploy it and put it to work! See your AI agent in action, whether in a chat interface or integrated into a business process. Once your agent is live, monitor agent behavior to flag anomalies and prevent security breaches.
Example: Use your invoice reconciliation agent to automatically compare and confirm values from purchase orders, goods receipt notes, and invoices, align delivery dates and item codes, and approve or flag discrepancies.
7. Assess and Iterate
Look back at what you defined as success and compare the results. Even small gains from end-to-end use cases in speed or accuracy can have big ripple effects across teams. Use these insights to refine and adapt your AI agent, making it even more effective over time.
Once you see the impact on a small part of the process, it’s time to think bigger. These early wins show how quickly value can be created and measured, and they pave the way for scaling. Imagine how long certain mission-critical tasks take to complete and the level of impact automating them could have on your team or organization. The real power and fastest path to ROI lies in agentifying business processes.
Revisit the list you made at the start: what other tasks could be automated with AI agents? Picture applying this across a larger workflow, your entire team, or even the whole company. As results multiply at scale, remember that none of it matters without trust. You need to secure and govern agents from the start so that you can grow with confidence and control.
Begin your agentic journey and start a free trial with Boomi Agentstudio.


 English
English 日本語
日本語