What you’ll learn:
● What intelligent processes are, and how they apply to business
● The application of human and non-human intelligence to automated processes
● More details on hyperautomation and how it enables AI-native business
As organizations evolve and innovate toward their AI ambitions, they must prioritize intelligent processes to stay competitive and efficient. As we progress in our Process Maturity Ladder (PML), as described in the first blog in this series, this article explores intelligent processes and examines the elements of human and machine intelligence as applied to business processes.
We’ll look at how rules, conditional logic, and the concept of hyperautomation can be woven into digital workflows and automated processes. This will set the stage for the next step in our series, where we will focus on optimized processes.
Contrasting Human and Machine Intelligence in Intelligent Processes
It’s essential to differentiate between human and machine intelligence. Both have their strengths and limitations and recognizing these differences is crucial for effectively embedding intelligence into processes.
Human intelligence is the foundation for many intelligent processes. It’s based on our innate cognitive abilities, such as critical thinking, problem-solving, pattern recognition, and emotional intelligence. Human intelligence excels at defining rules, making judgments, and generating insights based on experience and intuition. This, of course, carries over into work, as well.
Strengths of Human Intelligence in Process Automation
One particularly relevant aspect is the creation of human-defined rules. These are based on a deep understanding of the business domain and its requirements and serve as a guiding framework for process execution. Clear guidelines and expectations enable businesses to ensure consistency, accuracy, and compliance across workflows.
These rules form the foundation of how the enterprise governs itself, defines its entities (e.g., customers, departments, legal contracts, etc.), and communicates its values internally and to the world. In other words, rules govern how enterprises are organized: Conway’s Law.
Business Intelligence (BI) is another area where humans shine. It involves collecting, analyzing, and presenting business data to support decision-making. Humans excel at identifying trends, patterns, and anomalies in data – essential for making informed decisions to drive growth and innovation. Humans can ask the right questions and derive meaningful insights from complex data sets, enhancing BI’s value in intelligent processes.
Developing systems to compute multiple events in parallel, create, and enforce rules – called complex event processing (CEP) – is another example of human intelligence at work within intelligent processes. This kind of technology enables businesses to analyze and respond to multiple real-time events across various systems.
Human intelligence is crucial in defining the rules and patterns that govern event correlation and determining the appropriate responses to specific event combinations. By leveraging human expertise and intuition, CEP systems quickly identify and act on critical events, leading to more efficient and effective processes.
Human intelligence also is crucial in navigating the nuances of language and communication, understanding cultural contexts, and adapting processes to the business world.
Enterprises can effectively integrate human intelligence into their business processes by involving stakeholders, such as domain experts and cross-functional teams, in the development process. This way, intelligent processes will be designed with a deep understanding of the intricacies of language, culture, and business dynamics. They will be more adaptable and able to respond to changes. Ultimately, your enterprise will create processes that draw from the richness and complexity of human understanding of your business in your context.
Learn the best approach to applying human intelligence to new technologies with this Gartner® Report: How to Pilot Generative AI
Human Limitations in Process Automation
However, human intelligence has limitations. People are susceptible to cognitive biases, emotions, stress, and other factors that can influence our decision-making abilities. Processing large volumes of data and identifying patterns can be time-consuming and prone to human error, as well. In short, our puny earthling brains cannot keep up with the vast amounts of information compounding daily and processing that data at high speeds.
We also struggle with maintaining consistency in applying rules over time. If humans are fallible, so too is how we program logic into our processes. Human biases, fatigue, or emotions may lead to errors or inconsistencies in decision-making or building systems and software. This suggests that machine intelligence may be a better fit to take over at the limits of human ability.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms are the power behind machine intelligence. These technologies enable machines to learn from data, recognize patterns, and make predictions or decisions based on historical information. It excels at processing and analyzing vast amounts of data quickly, identifying patterns, and applying – even automatically creating – rules consistently and accurately.
Intelligent algorithms can sift through large datasets quickly and efficiently, often uncovering hidden patterns or relationships that may not be apparent to human observers. They can also be programmed to apply rules without being influenced by biases or emotions, resulting in more consistent decision-making.
However, AI has limitations. Algorithms can sometimes be opaque, making understanding their inner workings or the reasoning behind decisions challenging. Additionally, AI systems may need help to adapt to new or unexpected situations that deviate from the patterns in their training data. But these limitations are waning as recent advances in multi-modal models become available.
Everything in Balance
In intelligent processes, it’s crucial to balance human and machine intelligence. Organizations can optimize processes and make better decisions by combining their unique strengths. Human intelligence provides the context, understanding, and intuition needed to guide and refine AI-driven processes, while machine intelligence contributes to speed, accuracy, and scalability.
This is why now is the time to examine your processes and mature them along the Process Maturity Ladder as quickly as possible. Your competitors are because customers demand it.
AI-Ready, AI-Infused, and AI-Native Processes
Humans are still part of the loop as we focus on machine intelligence. Let’s define the progress from AI-ready to AI-infused and eventually AI-native processes. We can assume that human intelligence is present in some form within each process category. Achieving symbiosis between human and machine intelligence is vital, and embracing these stages of AI fruition is the key to unlocking the full potential of this collaboration.
Maturing your processes along the PML is a strategic move to stay ahead of the competition and a response to increasing customer expectations. Organizations harness the power of both human and machine intelligence by transitioning from AI-ready to AI-infused and, ultimately, AI-native processes. The result is more effective and adaptable workflows, better decision-making, and improved customer satisfaction.
Let’s dive deeper into how you can begin transforming your processes to meet future demands.
AI-Ready Processes
AI-ready processes are workflows and operations prepared to incorporate artificial intelligence. These processes have a strong foundation in data quality, process automation, and infrastructure, allowing for the integration of AI technologies. Examples of AI-ready processes include:
- Customer support ticket routing. An AI-ready process might involve simple automation to route incoming support tickets based on pre-defined rules, such as keywords or customer profiles. Human intelligence could create and update the pre-defined rules based on observations of ticket trends as well as handle complex or sensitive issues that require empathy and deeper understanding.
- Order processing. In an AI-ready order processing system, automated steps might include data entry and validation, while human intelligence is applied to handle exceptions or discrepancies, ensuring smooth order fulfillment. Humans can provide additional insights on vendor relationships, special order requirements, or delivery preferences based on their experience and understanding of customer needs.
- Customer support. Basic automated processes like email filtering and ticket assignment can be used for AI-ready customer support, but human agents are still responsible for understanding and resolving customer issues. Human intelligence plays a role by leveraging empathy, active listening, and cultural understanding to provide personalized and compassionate support.
- Inventory management. AI-ready inventory management could automate routine stock monitoring and reordering tasks, with human oversight ensuring that stock levels are maintained accurately, and supply chain disruptions are addressed. Human intelligence comes into play when assessing market trends, seasonal demands, or unique product requirements that may affect inventory planning.
AI-Infused Processes
AI-infused processes are workflows enhanced by integrating artificial intelligence technologies. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and other AI capabilities, these processes become more efficient, intelligent, and adaptable to changing conditions. They combine the strengths of human and machine intelligence, resulting in improved decision-making, optimized operations, and better overall performance. Examples include:
- Predictive maintenance. AI-infused processes use machine learning algorithms to analyze sensor data from equipment, allowing organizations to predict potential failures and schedule maintenance proactively. Human intelligence plays a role in interpreting the results of the predictive algorithms, determining the most appropriate maintenance actions, and providing feedback to improve the accuracy and relevance of the predictions over time.
- Marketing campaigns. AI-infused marketing processes can leverage machine learning algorithms to predict customer behavior and preferences, allowing human marketers to tailor their strategies and messaging for more effective, personalized campaigns. Human intelligence is essential for creative ideation, understanding cultural nuances, and making strategic decisions that align with overall business objectives.
- Talent acquisition. AI-infused talent acquisition can involve natural language processing and machine learning to analyze candidate resumes and identify the best matches, with human recruiters handling interviews and making final hiring decisions. Human intelligence is necessary for assessing soft skills, cultural fit, and long-term potential that may not be apparent in resumes alone.
AI-Native Processes
AI-native processes are workflows and operations designed from the ground up with artificial intelligence as a core component. These processes prioritize using AI technologies in decision-making, optimization, and execution. AI-native processes fully harness the potential of AI to drive innovation, streamline workflows, and provide a competitive edge in the market. Some processes include:
- Fraud detection. AI-native processes in financial services use advanced AI techniques, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning, to identify and adapt to evolving fraud patterns, providing real-time prevention and risk management. Human intelligence can analyze and interpret the output of AI models, identify false positives or negatives, and provide feedback for continuous improvement. Human expertise also is necessary for understanding the broader financial context and implementing appropriate risk management strategies.
- Predictive maintenance. AI-native predictive maintenance processes utilize advanced machine learning models to anticipate equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively with minimal human intervention. However, human intelligence can evaluate the implications of maintenance decisions, oversee safety protocols, and provide insights on potential improvements based on historical data and practical experience.
- Sentiment analysis. In an AI-native sentiment analysis process, natural language processing and deep learning techniques automatically understand and categorize customer feedback across various channels. Human intelligence can interpret complex or ambiguous feedback, address high-priority concerns, and guide overall customer satisfaction strategies based on empathy and understanding.
- Supply chain optimization. AI-native supply chain optimization processes leverage AI to analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, automating decision-making for optimal routing, inventory levels, and supplier selection. Human intelligence can provide oversight for high-level strategy, evaluate the impact of major disruptions, and bring a wealth of experience in managing supplier relationships and navigating unforeseen challenges.
Whether AI-ready, AI-infused, or AI-native, incorporating artificial intelligence into your organization’s processes is essential for remaining competitive and meeting customer demands. But to truly unlock the potential of AI and create an intelligent enterprise, organizations must go beyond merely integrating it into individual processes. This is where hyperautomation comes into play.
By combining multiple advanced technologies, hyperautomation enables businesses to automate entire processes, fostering agility, efficiency, and resilience while fully leveraging the power of AI. Let’s explore how hyperautomation elevates intelligent processes to the next level.
Hyperautomation: The Next Step in Intelligent Processes
Hyperautomation is an emerging concept that utilizes multiple advanced technologies to automate end-to-end processes rather than individual tasks. Hyperautomation blends AI, ML, integration platforms (including iPaaS), API management, robotic process automation (RPA), process mining, intelligent document processing (IDP), and intelligent business process management (iBPM) to enable businesses to become more agile, efficient, and resilient. This concept builds on the foundation of intelligent processes and represents a crucial step toward an AI-native enterprise.
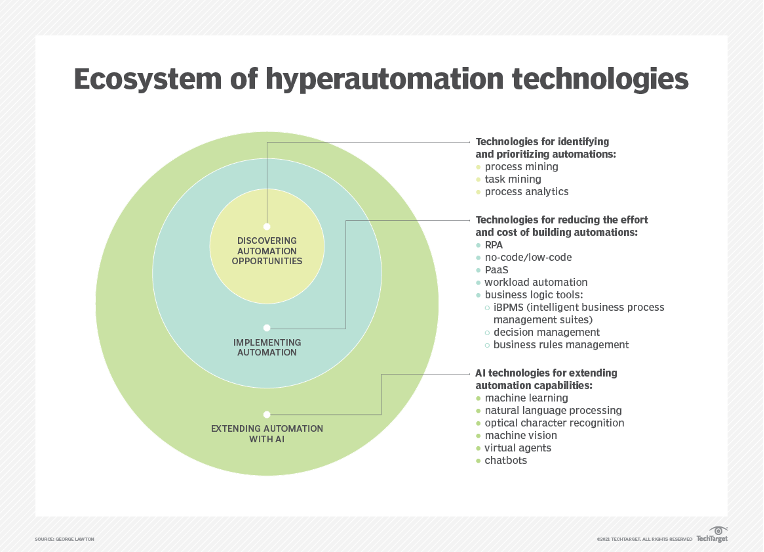
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchcio/definition/hyperautomation
What Is Hyperautomation, and How Does It Help Enterprises?
Hyperautomation incorporates AI and ML technologies to create self-adapting, self-optimizing processes to extend beyond traditional automation techniques. This approach allows organizations to address the complexity of modern business processes, automate a broader range of tasks, and achieve greater operational efficiency.
Hyperautomation takes a holistic approach by combining advanced technologies to enhance decision-making, anticipate potential challenges, and adapt processes by integrating human and machine intelligence. It also allows businesses to leverage the full power of AI while maintaining the richness and complexity of human understanding, ultimately resulting in more effective and adaptable workflows.
Organizations using hyperautomation can see significant improvements by streamlining end-to-end processes, reducing manual labor, and increasing productivity through low-code tools and cross-cloud integration. It also improves accuracy with the help of AI and ML algorithms, which analyze data and make predictions, thereby reducing errors and enhancing decision-making quality.
Hyperautomation fosters enhanced agility by allowing real-time process adaptation to changing market conditions or customer demands. Organizations can also save on labor costs and operational expenses while achieving greater resilience in the face of disruptions like market fluctuations, technology failures, or external threats.
Why Hyperautomation Is Necessary for Intelligent Processes
Hyperautomation allows organizations to quickly adapt to rapid changes in the business environment, scale automation efforts across the entire enterprise, and empower decision-making through AI and ML technologies. Hyperautomation facilitates innovation, enabling organizations to improve their products, services, and customer experiences by streamlining processes, freeing up resources, and ultimately providing a significant competitive advantage.
Still, it also presents potential downsides. Implementing hyperautomation can be complex and require significant investment in technology and training. Over-reliance on automation can decrease human involvement, potentially reducing creativity and critical thinking in decision-making processes. There also may be concerns related to job displacement as automation takes over repetitive tasks.
Enterprises need to weigh the pros and cons carefully. By assessing your specific needs, processes, and goals, you can make informed decisions on how much you adopt hyperautomation in your enterprise.
You can still gain significant advantages without owning the full hyperautomation palette to implement AI-ready, AI-infused, or AI-native processes. Taking stock of your business or mission-critical processes, automating them, and making them intelligent will go a long way toward making the business more competitive.
Still, if you can afford — or said another way: if you cannot afford not — to have the whole gamut of hyperautomation, you will have the necessary resources to make any of your processes intelligent, optimized, and potentially disruptive. This will allow your organization to compete against competitors using AI in their processes while having an unfair advantage against those who do not.
Recap and Look To Optimize
Intelligent processes play a critical role in the Process Maturity Ladder by bridging the gap between automated and optimized processes.
Businesses can create more effective, adaptable, and resilient workflows by harnessing the power of both human and machine intelligence. People provide context, understanding, and intuition to refine AI-driven processes, while machines contribute to speed, accuracy, and scalability. Together, they help organizations meet the increasing demands of customers and stay competitive in the market.
As businesses integrate AI technologies into their operations, they must strategically incorporate human intelligence to ensure their processes remain adaptable and effective.
Meanwhile, hyperautomation is a powerful tool for implementing intelligent processes by automating end-to-end processes and leveraging AI, machine learning, and other advanced technologies. There are potential downsides to consider, such as complexity and job displacement, so enterprises must weigh those risks against the benefits to determine the right level of hyperautomation adoption.
Intelligent processes represent a crucial step in the journey toward optimized processes. By combining human and machine intelligence and leveraging hyperautomation, organizations can create robust, adaptable, and efficient workflows that drive business success.
Stay tuned for the next article in our series, where we’ll dive deeper into optimized processes, exploring their potential benefits, challenges, and real-world applications.
Please contact us for more information on how Boomi can help guide you along your process maturity ladder.
Check out the earlier posts in our series:


 English
English 日本語
日本語